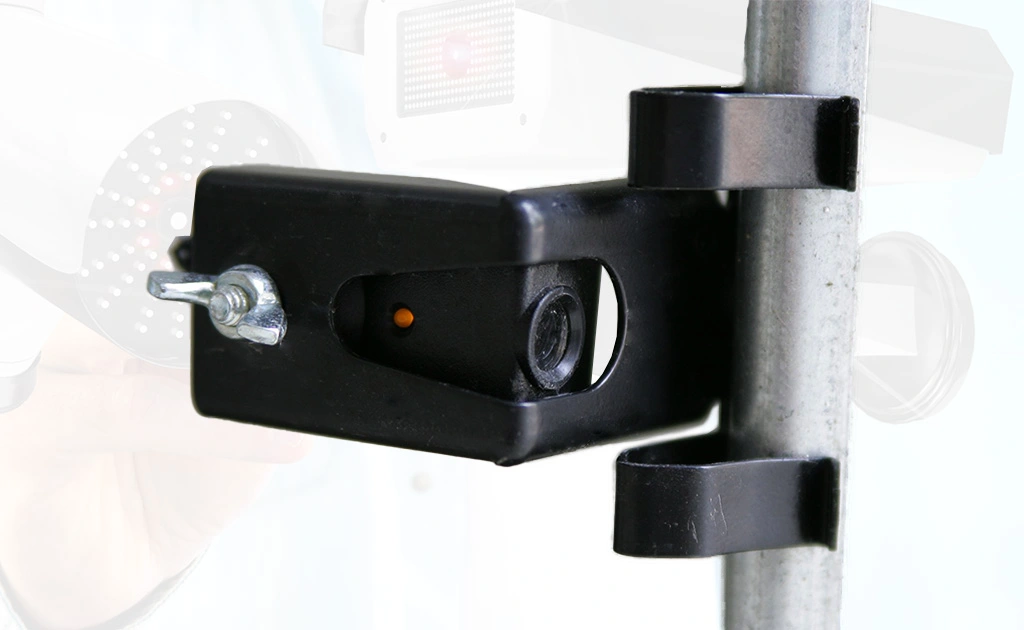
Photo eye sensors are essential in various industries, playing an important role in both automation and safety. These sensors, also known as photoelectric sensors, detect the presence or absence of an object using light. You’ll find them in manufacturing, security systems, and everyday items like garage door openers. Understanding how does a photo eye sensor work can help you choose the right sensor for your needs.
A photo eye sensor works by emitting a light beam. When something interrupts or reflects this beam, the sensor triggers an action. This simple yet powerful technology makes photo eye sensors a very important part of many automated systems. Knowing how does a photo eye sensor work can give you a better appreciation what they are used for and how you can benefit from them.
From assembly lines to home security, these sensors are a great way to boost efficiency and safety. As technology progresses, photo eye sensors are becoming even more precise and reliable. This guide will take a look into the workings, types, applications, and future trends of photo eye sensors, offering valuable insights for anyone interested in this amazing technology.
A photo eye sensor is a device that detects the presence or absence of an object using light. It’s a type of photoelectric sensor that plays an important role in various automation and safety applications. But what is photo sensor exactly? Let’s break it down.
A photo eye sensor consists of three main components: a light emitter, a receiver, and a signal processor. The emitter sends out a beam of light, which can be either visible or infrared. The receiver is positioned to detect this beam. When an object interrupts or reflects the light beam, the receiver senses this change and sends a signal to the processor. The processor then triggers a specific action based on the sensor’s design and application.
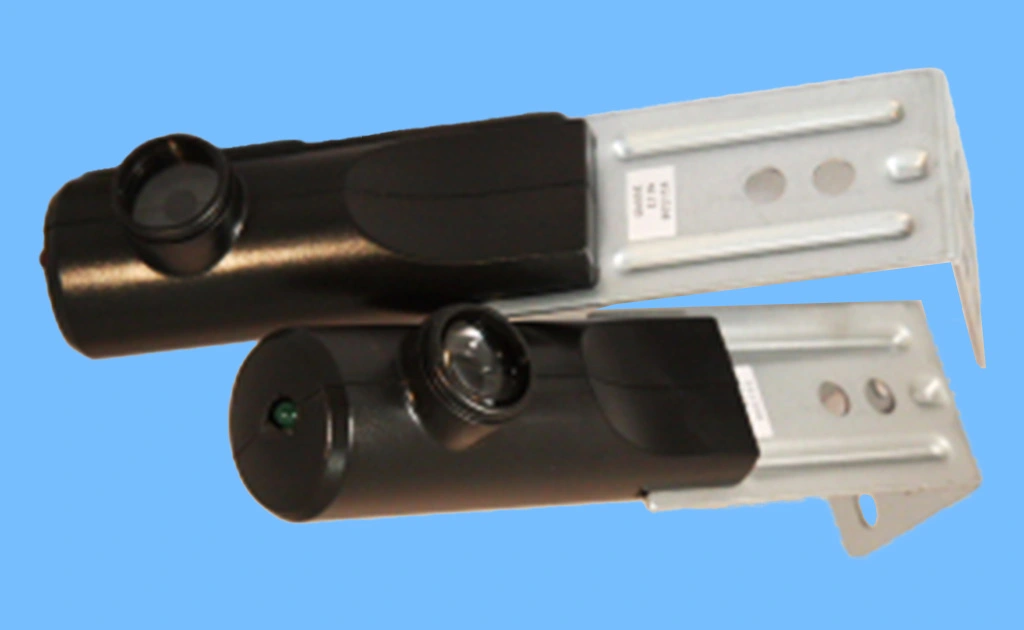

These sensors are incredibly versatile and are used in numerous different industries. In manufacturing, they are commonly found on assembly lines to detect the position of parts, ensuring accurate production processes. They are also widely used in packaging industries to count items and verify the presence of packaging materials.
In the world of security, photo eye sensors are used in systems like automatic doors and gates. When the light beam is interrupted, it signals the door to open or the gate to stop closing, preventing accidents and maximizing safety. Garage door openers also rely on these sensors to detect obstacles, ensuring the door doesn’t close on something or someone.
Retail environments use photo eye sensors for tasks such as people counting and product detection. For example, they can help store owners understand customer traffic patterns or alert staff when a product is removed from the shelf.
How Does a Photo Eye Sensor Work?
How does a photo eye sensor work? A photo eye sensor works by emitting a light beam and detecting its interruption or reflection to trigger a specific action. The sensor consists of an emitter that sends out the light and a receiver that continuously monitors it. When an object disrupts the light beam—whether by blocking it or reflecting it—the sensor detects this change and sends a signal to its processor. The processor then interprets the signal to initiate the designated action, such as stopping machinery, opening a door, or sending an alert. Various types of photo eye sensors—through-beam, retro-reflective, and diffuse—operate based on different detection mechanisms.
To understand how does a photo eye sensor work, it’s important to start with the basics. A photo eye sensor operates by emitting a light beam, detecting its interruption or reflection, and then triggering a specific action based on this detection.
Light Source Emission
To understand how does a photo eye sensor work, it’s important to start with the basics. A photo eye sensor operates by emitting a light beam, detecting its interruption or reflection, and then triggering a specific action based on this detection.
Detection Mechanism
The next critical component is the receiver, positioned to detect the emitted light beam. The receiver is designed to sense the light continuously. In a clear path, the receiver constantly detects the light from the emitter, indicating no presence of an object in the path.
Interruption or Reflection Triggering
When an object comes into the path of the emitted light beam, it either interrupts the beam or reflects it back to the sensor, depending on the type of photo eye sensor used. There are three main types of photo eye sensors:
Through-Beam Sensors: In this type, the emitter and receiver are placed opposite each other. The presence of an object interrupts the light beam, causing the sensor to trigger an action.
Retro-Reflective Sensors: Here, the emitter and receiver are housed together, and a reflector is placed opposite them. The light beam travels to the reflector and back to the sensor. An object in the path reflects the light back, causing the sensor to trigger an action.
Diffuse Sensors: In this type, the emitter and receiver are housed together, but no reflector is used. The light beam is emitted towards the target area, and the object itself reflects the light back to the sensor, triggering an action.
Output Signal Processing
Once the light beam is interrupted or reflected, the receiver detects this change. The detection mechanism sends a signal to the sensor’s processor, which then interprets this signal and triggers the designated action. This could be anything from stopping a machine on a production line to opening a door or sending an alert.

Types of Photo Eye Sensors
When looking into the different types of photo eyes, it’s essential to understand the different designs and how they function. There are three primary photo eye sensor types: through-beam, retro-reflective, and diffuse. Each type has unique characteristics and is best suited for specific jobs.
Through-Beam Sensors
When looking into the different types of photo eyes, it’s essential to understand the different designs and how they function. There are three primary photo eye sensor types: through-beam, retro-reflective, and diffuse. Each type has unique characteristics and is best suited for specific jobs.
Best used for
Industrial Automation: Used on assembly lines to detect parts and ensure they are in the correct position.
Security Systems: Used in perimeter security to detect intrusions when someone crosses the light beam.
Elevator Doors: Prevent doors from closing if an object or person is detected in the doorway.
Retro-Reflective Sensors
Retro-reflective sensors have the emitter and receiver housed together in one unit. They work with a reflector placed opposite the sensor. The emitter sends out a light beam that is reflected back to the receiver. When an object blocks the light beam, the sensor detects the absence of the reflected light and triggers an action. These sensors are easy to install and require only one wiring location, which makes them easier to setup.
Best used for
Automated Gates: Used to detect vehicles or pedestrians, preventing gates from closing on them.

Packaging Lines: Ensure that products are correctly aligned and packaged by detecting their presence or absence.
Warehouse Management: Monitor and control the movement of items on conveyor belts.
Diffuse Sensors
Diffuse sensors also have the emitter and receiver housed together. Unlike retro-reflective sensors, they do not use a reflector. Instead, the emitted light beam is directed at the target area, and the object itself reflects the light back to the receiver. The sensor detects this reflection and triggers an action. These sensors are ideal for detecting objects at shorter distances and are less affected by dirt or misalignment.
Best used for:
Retail Stores: Count the number of people entering or exiting, providing valuable data for managing store traffic.
Robotics: Used in robotic arms to detect objects and guide their movements accurately.
Food and Beverage Industry: Ensure the correct placement and presence of items on production lines.
Key Specifications and Features of Photo Eye Sensors
When choosing a photo eye sensor, understanding its key specifications and features is very important. These aspects determine the sensor’s performance and whether it is suitable for a specific application.
Sensing Range
The sensing range of a photo eye sensor refers to the maximum distance at which the sensor can detect an object. This range varies based on the type of sensor and its intended application. For instance, through-beam sensors typically have the longest sensing range, often extending several meters, making them perfect for long-distance applications. On the other hand, diffuse photo eye sensors have a shorter sensing range, usually up to a few centimeters or meters, suitable for close-proximity detection.
Response Time
Response time is the speed at which the sensor detects an object and triggers an action. A faster response time is essential for high-speed applications where quick detection is critical. For example, in fast-moving production lines, a sensor with a response time of a few milliseconds ensures accurate and fast detection, which can help prevent delays and errors.
Environmental Resistance
Photo eye sensors often operate in challenging environments, so their ability to withstand conditions like dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures is important. Many sensors come with solid housings that provide protection against these elements. For instance, diffuse photo eye sensors used in the food and beverage industry are designed to resist washdowns and exposure to chemicals, which ensures reliable performance and enhanced longevity.
Applications of Photo Eye Sensors
Photo eye sensors are versatile tools that are used across various industries to enhance automation, safety, and efficiency. Here are some interesting sensor examples of how these sensors are used in different industries:
Logistics and Warehousing
In logistics and warehousing, photo eye sensors play an important role in managing inventory and streamlining operations. These sensors are used in automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) to detect the presence and position of items on shelves. They ensure that goods are correctly placed and retrieved, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Also, photo eye sensors are used in conveyor systems to monitor the flow of packages, preventing jams and ensuring operations continue to run smoothly.
Agricultural Technology
Agriculture has seen significant advancements with the integration of photo eye sensors. These sensors are used in smart farming equipment to monitor the growth and health of crops. For instance, photo eye sensors can detect the presence of plants and measure their growth rate by analyzing the reflection of light. This data helps farmers optimize irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting processes, which can lead to better crop yields and improved resource management.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, photo eye sensors are used in various diagnostic and therapeutic devices. For example, in automated blood analyzers, photo eye sensors detect the presence and quantity of blood samples in test tubes, ensuring accurate processing and better analysis. These sensors are also used in infusion pumps to monitor the flow of medication, preventing over or under-dosage and ensuring patient safety.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies on photo eye sensors for several applications, from manufacturing to safety systems. In manufacturing, these sensors are used in robotic assembly lines to ensure precise placement of parts and components. In vehicles, photo eye sensors are part of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), where they detect obstacles and pedestrians, contributing to features like automatic emergency braking and adaptive cruise control.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, photo eye sensors are essential for quality control and packaging processes. These sensors can detect the presence of containers and ensure they are correctly filled, sealed, and labeled. They are also used in sorting systems to identify and remove defective products, maintaining high standards of quality and safety.
Retail and Customer Experience
Retailers use photo eye sensors to enhance the shopping experience and improve store operations. For example, sensors are used in interactive displays that light up or play a video when a customer approaches, creating an engaging shopping experience. They are also used in self-checkout systems to detect items placed in the bagging area, ensuring more accurate transactions.

Installation and Maintenance of Photo Eye Sensors
In order to ensure the best possible performance and the longest lifespan, it is important that your photo eye sensor installation is done properly. Here’s what you need to know:
Step 1: Choose the Right Location
Select a suitable location where the sensor will have a clear line of sight to detect the target object. Ensure there are no obstructions that could interfere with the light beam.
Step 2: Mount the Sensor
Secure the sensor firmly in place using brackets or mounting hardware provided by the manufacturer. Ensure that the sensor is aligned correctly with the target area or reflector.
Step 3: Align the Emitter and Receiver
For through-beam and retro-reflective sensors, alignment is critical. Use the alignment indicators or tools provided to ensure that the emitter and receiver (or reflector) are properly aligned. This ensures that the light beam travels accurately between them.
Also, proper alignment of other garage door sensors is very important. You can check out our other guide on how to align other garage door sensors.
Step 4: Connect the Wiring
Follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram to connect the sensor to your control system. Ensure that all connections are secure and insulated to prevent any electrical issues.
Step 5: Adjust the Sensitivity
Set the sensitivity of the sensor according to your application’s requirements. This may involve adjusting the potentiometer or using a setup button, depending on the sensor model.
Step 6: Test the Sensor
After installation, test the sensor by placing objects in its path to ensure it detects correctly. Adjust the alignment and sensitivity if necessary to achieve optimal performance.
Essential Maintenance Tips
Regular Cleaning: Keep the sensor’s lenses clean and free from dust, dirt, and debris. Use a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solution to gently wipe the lenses. Regular cleaning helps maintain accurate detection and prevents false triggers.
Check Alignment: Periodically check the alignment of through-beam and retro-reflective sensors. Environmental factors such as vibrations and temperature changes can cause misalignment over time. Realign the sensors if necessary to ensure consistent performance.
Inspect Wiring: Regularly inspect the wiring connections for signs of wear or damage. Ensure that all connections are secure and replace any damaged cables to prevent electrical issues.
Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on the sensor’s performance. If you notice any irregularities or false triggers, investigate and address the issue right away. This may involve cleaning the sensor, adjusting the sensitivity, or checking the alignment.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Stick to the maintenance guidelines provided by the sensor’s manufacturer. These guidelines are tailored to the specific model and can help you get the best performance and longest life out of your sensor.
How to Ensure the Longevity of your Sensor
Protect from Environmental Factors: If the sensor is used in harsh environments, consider using protective housings or covers to shield it from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Scheduled Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to check and service the sensors. This proactive approach helps in early detection of potential issues and extends the sensor’s lifespan.
Training: Ensure that personnel handling the sensors are properly trained. Proper installation and maintenance techniques can significantly impact the sensor’s performance and longevity.
Common Troubleshooting and Solutions for Photo Eye Sensors
Photo eye sensors are reliable, but like any technology, they can sometimes encounter issues. Knowing common problems and how to fix them can save time and maintain efficiency. Moreover, the sensor can often be bypassed, which is not a permanent solution. Here are some typical issues and practical photo eye sensor troubleshooting tips.
Sensor Not Detecting Objects
- Check Alignment: Ensure the emitter and receiver are properly aligned. Use alignment tools or indicators to make precise adjustments.
- Clean the Lens: Dirt and debris on the sensor’s lens can block the light beam. Clean the lens with a soft cloth and a suitable cleaning solution.
- Adjust Sensitivity: Increase the sensor’s sensitivity setting if it’s too low to detect objects.
False Triggers
- Eliminate Interferences: Check for reflective surfaces or other light sources that might interfere with the sensor. Remove or shield these sources if possible.
- Reduce Sensitivity: Lower the sensitivity setting to prevent the sensor from reacting to minor disturbances.
- Use Background Suppression: If using a diffuse sensor, ensure it is equipped with background suppression to distinguish between the target object and background.
Intermittent Detection
- Secure Mounting: Ensure the sensor is firmly mounted and not subject to vibrations or movement.
- Inspect for Obstructions: Check the sensor’s path for any objects that might intermittently block the beam.
- Check Power Supply: Ensure the sensor is receiving a consistent power supply without fluctuations.

Alignment Problems
- Re-align the Sensor: Use alignment indicators or tools to re-align the emitter and receiver accurately.
- Stabilize the Mount: Ensure the mounting brackets or hardware are stable and secure to prevent misalignment due to vibrations or movements.
- Regular Checks: Periodically check the alignment, especially in environments with high vibrations or temperature changes.
Wiring Issues
- Inspect Connections: Regularly check all wiring connections for signs of wear or damage. Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated.
- Replace Damaged Cables: Replace any worn-out or damaged cables immediately to maintain reliable performance.
- Follow Wiring Diagrams: Follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram to ensure correct and secure connections.
If you still don’t get good results after trying all the above troubleshooting steps, you may need to replace the sensor in the future. Check out our simple guide on how to replace a garage door sensor.
Advantages of Photo Eye Sensors
Understanding how does a photo eye sensor work, and what benefits that they offer is very important. Their accuracy ensures precise detection of objects, which is important in automation and safety applications. They are also reliable, functioning consistently even in challenging environments.
Cost-effectiveness is another key advantage, as these sensors reduce the need for manual monitoring and decrease the likelihood of errors, leading to savings on labor and production costs.
Limitations of Photo Eye Sensors
Despite their many benefits, photo eye sensors have some limitations. They can be sensitive to environmental conditions such as dust, dirt, and ambient light, which may affect their performance. To minimize this, regular maintenance and proper installation are important.
Another limitation is their limited detection range in some models, which might not be suitable for all applications. Choosing the right type of sensor, such as through-beam for long distances or diffuse for short-range detection, can help address this issue.
Expert Tips for Long-Use Photo Eye Sensors
To maximize the lifespan and efficiency of your photo eye sensors, follow these expert tips.
- First, ensure proper alignment and regular cleaning to prevent dust and debris from interfering with performance.
- Regularly check connections and wiring for signs of wear.
- Understand how does a photo eye sensor work to diagnose and fix issues promptly.
- Use protective housings in harsh environments to shield sensors from damage.
- Lastly, implement a routine maintenance schedule to keep sensors in top condition.
Understanding UL 325 Compliance: What It Means for Your Gate Operator
When it comes to gate operators, safety isn’t just a feature—it’s a legal requirement. UL 325 is the gold standard in safety regulations for automated gate systems in the United States, designed to protect users from potential hazards. These guidelines are not optional; they’re the law, ensuring that every installation meets rigorous safety criteria.
So, what does this mean for you? First and foremost, if your current gate operator doesn’t comply with UL 325, we can’t perform repairs on it as-is. Operating non-compliant equipment not only puts you at risk, but it also leaves us with limited options. The safest path forward is to either replace the outdated unit or install the necessary safety sensors to bring it up to code.
The good news? Every operator we install already meets these stringent UL 325 standards. This means you can trust that your system is as safe as it is functional, giving you peace of mind and full compliance with the law.
Remember, safety isn’t just about avoiding fines or legal trouble—it’s about protecting people. That’s why UL 325 compliance is non-negotiable for us, and it should be for you too.
Future Trends in Photo Eye Sensor Technology
Photo eye sensor technology continues to evolve, bringing exciting advancements and new applications. One emerging trend is the integration of smart sensors with IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities. These smart sensors can communicate data in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and improved decision-making.
Additionally, miniaturization is making sensors smaller and more versatile, allowing them to be used in compact and intricate systems.
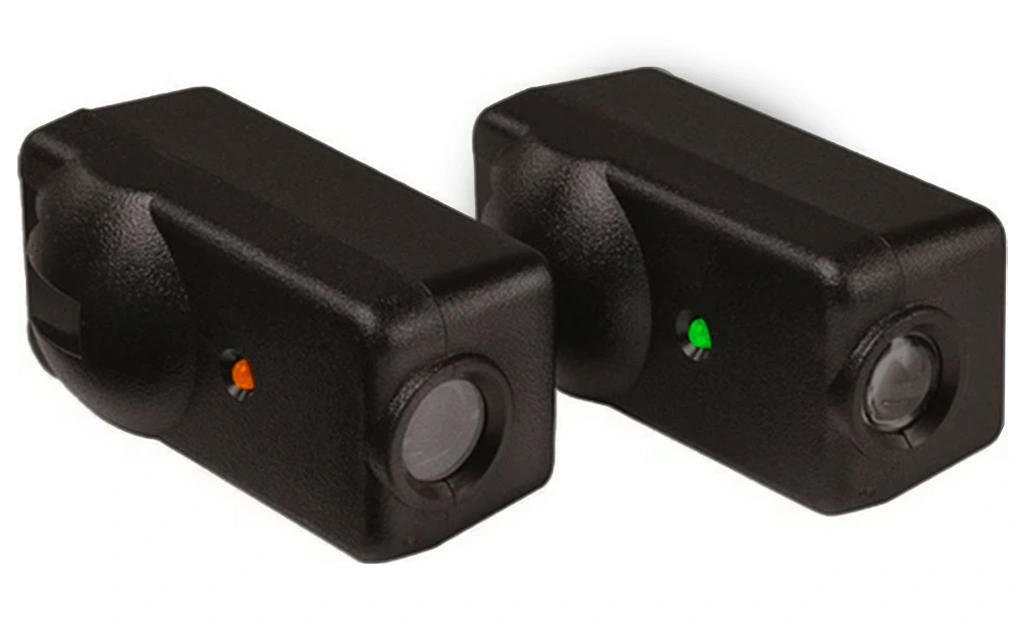

Another innovation is the development of multi-spectral sensors that can detect a wider range of wavelengths, enhancing accuracy and reliability in diverse environments. AI and machine learning are also being incorporated to improve object detection and differentiate between objects more precisely.
Future applications include advanced robotics, where sensors provide better guidance and safety, and in healthcare, where they could be used for more precise diagnostics and monitoring. These trends further expand the capabilities of how does a photo eye sensor work, making them even more important to modern technology.
The Essentials of Photo Eye Sensors
Understanding how does a photo eye sensor work is important for optimizing their use in various applications. We’ve covered the basic principles, different types, key specifications, installation tips, troubleshooting, advantages, limitations, and future trends. These sensors are indispensable in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare because of their accuracy, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.







